salt-water-powered 'maritime' mobility

Hyundai Motors has raised its anchor beyond the ground to the sea.
The plan is to launch a platform with partners by 2023.
The project was confirmed to have been reported to the highest levels of management.
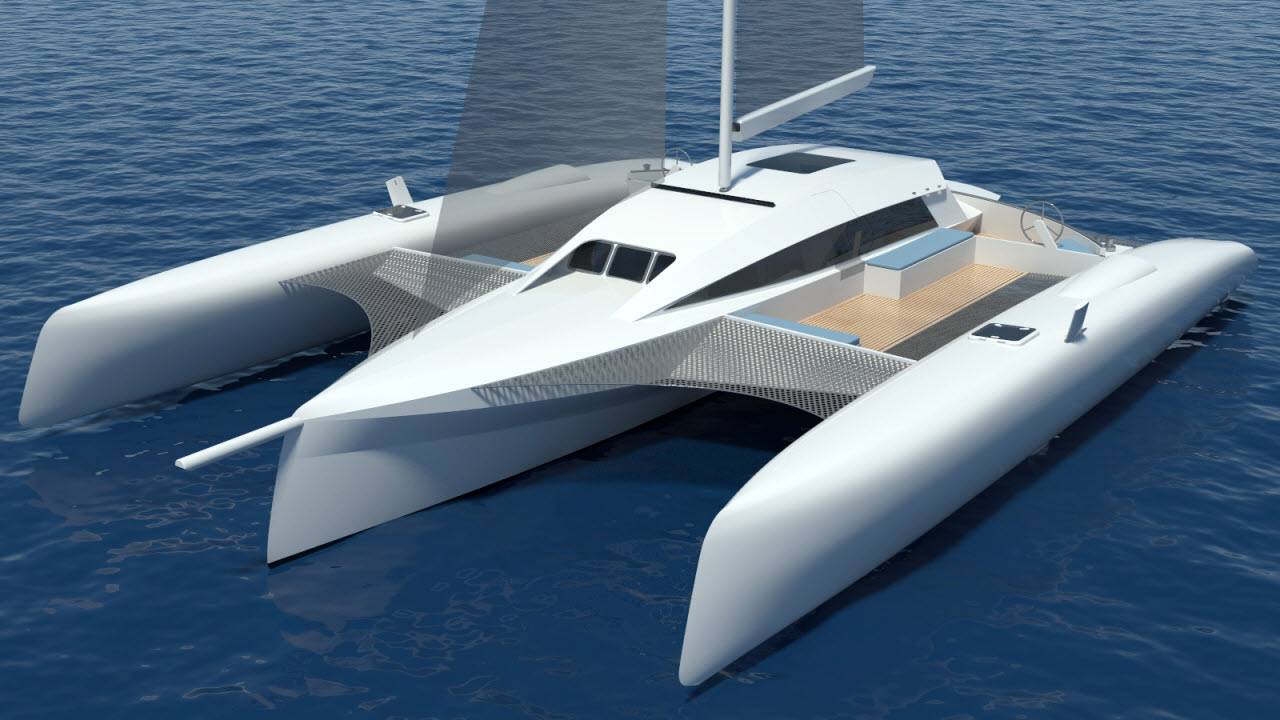
According to the shipbuilding industry on the 27th, Hyundai is developing a yacht 15-20 meters long with its hydrogen fuel cell.
The yacht is in the form of a 'trimaran' with two smaller hulls connected to either side of the central hull. As each hull breaks down seawater into hydrogen, the hydrogen fuel cells mounted inside generate electricity, and the propellers spin to drive the yacht.
The power required to extract hydrogen from seawater is supplied by solar cells installed in the sails and two vertical wind generators attached to the hull. The price per unit is 45 billion.
" If you load a container, you can be a container ship, if you carry passengers, if you install a passenger ship, if you install a garbage disposal system, it can be a garbage disposal ship, and its use depends on what you are uploading," he said. They seem to be aiming to 'standardize' the mobility platform."
Drone, an autonomous driving-based mode of transportation, at the Susosoviability Show last September. The trailer drone is a new concept of transport mobility with a trailer on top of 2 'e-Bogie ' with hydrogen fuel cells and fully autonomous driving technology, capable of driving more than 1,000 km on a single charge .
There are many 20-30-year-old diesel-engined vessels on the near coast, which are polluting the environment to the point where they can't even get their hands on it." There's a lot of demand for it , but it's about how economically (Hyundai) produces (its maritime mobility platform)." "Since the flow has already shifted to electric vehicles and the hydrogen passenger car NEXO has a lot of 'cost-effectiveness' in terms of infrastructure construction, the direction is to target the hydrogen truck, hydrogen tram and hydrogen vessel markets."
The reason why hydrogen vessels are not currently commercialized is because of the technological challenges as well as the economics. Because hydrogen vessels receive air resistance hundreds of times higher than electric vehicles, they must produce electricity at large capacities, constantly, and reliably. However, by building a large hydrogen fuel cell and a battery to assist it, the range of magnetic fields can also be widened, causing the malfunction of components in repair vessels, such as sensors and semiconductors.